What are brake pads?
Brake pads are part of your vehicle's braking system. They come into friction with both sides of the surface of the rotating brake disc to slow it down and stop its rotation. They therefore serve to stop your vehicle.
Features
Brake pads must:
- Withstand operating temperatures of up to 800°C.
- Maintain their level of friction regardless of speed, pressure or temperature.
- Resist wear without attacking the friction track on the brake disc.
- Recover their level of friction when wet.
- They mustn’t make a noise.
Composition
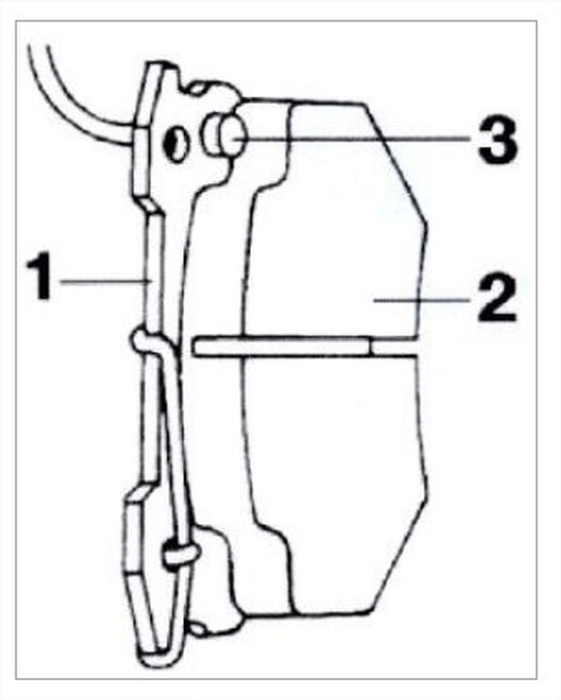
In general, a brake pad consists of the following components:
1: metal backing
2: brake lining
3: wear warning studs (found on contemporary vehicles)
Quality "Original" Brake Pads versus "High Performance"
The only way to truly enhance the braking of your 4x4 is to replace "Original" quality brake pads with "High Performance" models. The distinction between the two lies in the composition of the linings, in the aramid fibres/graphite/metal powder blend that’s compacted to form them.
In the case of original equipment, automobile manufacturers instruct brake pad manufacturers to produce models with a "decent" coefficient of friction, while being less aggressive towards the discs to preserve them from rapid wear. These pads are considered hard, as their linings erode slowly.
Conversely, "High Performance" pads offer a higher coefficient of friction, resulting in improved efficiency. On the flip side, they are more "aggressive" on the cast iron. As a result, this type of brake pads will wear out faster. Instead of changing the brake pad every five sets, there’s a strong chance after three the cast iron will be completely grooved. This is why they are referred to as soft pads. Another disadvantage is their aggressiveness which puts the disc under more intense stress.

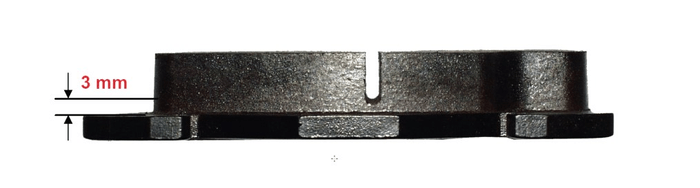
Brake pad wear
The surest way to check brake pads is to measure their thickness. In most cases, a visual check can be carried out by simply removing the wheel, but sometimes the brake pads have to be removed from the vehicle. Some brake pads are equipped with minimum thickness indicators to assess their wear. A brake check is recommended every 10,000 to 30,000 km depending on the use of your vehicle.
Most modern vehicles are equipped with a wear warning system. A warning light will come on the dashboard when the brake pads have reached the end of their life.
Examples of how to change brake pads
Possible Issues:
Complete or partial detachment of the friction lining from the backing plate.
| Causes | Results | Solutions |
|
|
|
Thermal Overload
The brake pad has been damaged due to overheating. The binders in the pad have been destroyed, and the lining fractures. The surface becomes porous and partially glassy.
| Causes | Results | Solutions |
|
|
|
Grooves in the Friction Lining
The surface of the lining exhibits grooves and significant wear edges.
| Causes | Results | Solutions |
|
|
|
Material Breaks and Lining Edge Fractures
The friction lining is damaged, with the coating broken along the edges.
| Causes | Results | Solutions |
|
|
|
Excessive Wear
The brake pads are heavily or partially worn down to the backing plate.
| Causes | Results | Solutions |
|
|
|

Uneven Wear of Brake Pads
The brake pads on one side of the wheel brake are unevenly worn.
| Causes | Results | Solutions |
|
|
|
Vitrification of the Friction Lining
The friction lining has a smooth surface, appearing polished and hard, reflecting light and resembling a glass-like surface. This defect typically occurs on new brake pads with a short operating life.
| Causes | Results | Solutions |
|
|
|
Surface Contamination of the Friction Lining
The brake pad has been contaminated by grease, oil, or other foreign substances.
| Causes | Results | Solutions |
|
|
|
PARTS
Brake pads for Toyota KDJ 120
Front brake pads
Rear brake pads


Find the brake pads to suit your vehicle:
Do it yourself, you'll be even prouder! To help you out, Euro4x4parts shares its know-how and expertise in mechanics through 4X4XPERT: new products, technical sheets, and personalized tutorials... You've got the keys!
And because we also learn from your experiences, your feedback is essential. Let us know your thoughts and suggestions by email: 4x4xpert@euro4x4parts.com
Check out our complete catalogue of 4x4 parts and accessories!
All the photos in our articles are taken on authorized roads or tracks, private land, or during supervised competitions. Let's all do our part to preserve the environment!
Please note: Euro4x4parts publishes this information to help its customers, but cannot be held responsible for the advice given here and their consequences when used.